Full Report about Pressure Gauge
Pressure Gauge:
The pressure gauge is a mechanical instrument that is widely used in industries for measuring of internal pressure of a vessel or system. Pressure gauges are offered in different sizes, shapes, and materials to meet the demand of specified applications and standards. Without pressure gauges, fluid power systems would be both unpredictable and unreliable.
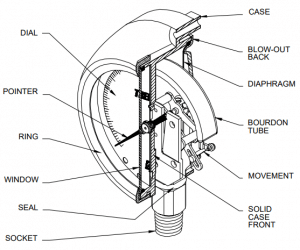
Figure 1: Pressure gauge and its components.
Types of Pressure gauge:
There are different types of pressure gauges.
- Bourdon tube
- Diaphragm type
- Bellow type
- Capsule type
In industries, we commonly used bourdon tube pressure gauges.
Bourdon tube operation is simple. They consist of a semicircular and flat tube of metal, fixed at one end and attached to a sensitive lever mechanism at the other. As pressure increases inside the tube, the force of the fluid attempts to straighten out the curved tube. The tube then pulls away from the lever, which is connected to the needle on the display, shows the pressure at the fluid port.
Metal bellows and diaphragms are also used as pressure-sensing elements. Because of the large deflections for small pressure changes, bellows instruments are particularly suitable for pressures below atmospheric. Two corrugated diaphragms sealed at their edges to form a capsule, which is evacuated, are used in aneroid barometers to measure atmospheric pressure.
Material:
The pressure range at which the gauge will be working is a primary selection factor for the type of material used to make the gauge. Gauges operating at higher pressures generally tend to be made of materials such as steel. When operating at lower pressures, they tend to be made of bronze.
Bourdon tube:
- Beryllium copper
- Phosphor bronze
- Steel and stainless steel
Socket:
- Brass
- Steel
- Stainless steel
Movement mechanism:
- Polycarbonate
- Brass
- Nickel silver
- Stainless steel
Gauge cases and dials:
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Steel
- Polycarbonate
- Polypropylene
Installation:
The pressure gauge should be installed in such a way as to avoid exposure to heat and vibration and to enable the dial indicator to be easily read.
These are the following things that we should keep in our mind during the installation of pressure gauges.
- Select the Right Gauge
- Apply Force on Wrench Flats
- Seal the Deal
- Use a Clamp Socket or Union Nut with Straight Thread
- Leave Space for Blow-out
- Vent the Gauge Case
Isolating Valves:
It is recommended that isolating valves be fitted with the gauge. This enables the gauge to be removed at any time for checking, recalibration, or replacing without interruption to the process.
Location
Vibration and extreme ambient temperatures can affect the dial reading of the pressure gauge. These areas should be avoided as much as possible. Also, it should be away from the part that needs frequent maintenance.
Mounting
A suitable thread sealant is required for NPT threads such as pipe dope or Teflon tape. Never use any part of the pressure gauge other than the wrench flats that are on the gauge socket.
Venting Procedures:
Due to pressure build-up, some may reflect a reading that is slightly “off zero”. To properly “vent” the pressure gauge, cut off the tip of the fill plug after you have installed the instrument. This allows the gauge to be equal to the atmospheric pressure.
Figure 2: Plugin pressure gauge.
Arrangement for Pressure gauges:
There are two ways by which we usually install pressure gauges. But in both cases, pressure gauges are in an upside position.
-
- Pressure gauge higher than tapping point.
- Pressure gauge lower than tapping point.
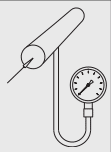
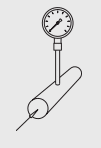
Figure 3: Pressure gauge higher (right) and lower (left) than tapping point.
Read Also: Ford is investing billions into electric vehicles
Threats and failure in Pressure gauge:
There are different failures that can occur in pressure gauges. Major of them are listed below:
- Vibration
- Pulsation
- Pressure Spikes
Vibration:
Vibration can affect the dial reading of pressure gauges and can reduce their life. Therefore, it’s best to look for gauges designed specifically for hydraulic applications.
These features include:
- A forged brass case to prevent resonant frequencies from destroying internal components
- A liquid-filled case to protect the gauge from vibration and extreme pressure cycles.
Although the liquid used in the gauge varies from application to application. Glycerin is commonly used and performs well in many conditions. The higher the viscosity of the liquid, the more it dampens the vibrations.

Figure 4: Glycerin in Pressure gauge.
Read Also: Thermowell and it’s explanation.
Pulsation
If pressures are expected to pulsate violently, oscillate with high frequency or occur with a sudden shock, a snubber should be considered. Winters’ snubbers incorporate sintered porous 316 stainless steel snubbing element with a large surface area to ensure long-term effectiveness on most pressure media. Snubbers are available in three viscosity classifications: heavy oil, water and air.

Figure 5: Snubbers for Pressure gauge
Pressure Spikes:
In certain applications, it is often unavoidable to experience pressure spikes. These spikes can often occur when a pump is being turned on or maybe when a valve opens up. A throttle screw, restrictor screw, or resistor can be used to avoid pressure spikes. Moreover, a pressure relief valve can be used. Pressure relief valves are small diversion valves mounted in between the instrument and the process gauge. The relief valve has an adjustable pressure setting on it. Once the pressure in the line reaches the pressure set point on the valve, the valve closes and diverts the pressure through its other orifice or into the atmosphere.

Figure 6: The pressure relief valve
References:
Here we have some useful vendor links that provided pressure gauges.
- https://en.wika.com/products_pressure_gauges_en_co.WIKA
- https://www.globalsources.com/Pressure-gauge/Pressure-Gauge-1129625641p.htm?pos_dd=prod_PrdtDDImage_1_0#1129625641
- http://www.strongmac.cn/en/product/product-41-909.html
- https://www.pressuregaugeindia.com/economical-ss-304-pressure-gauges.html


0 Comments